Transformation in Design Engineering:
With the transition of finite element analysis software from hardware to discrete graphics card computer over the last two decades, the job of design engineers has changed dramatically.
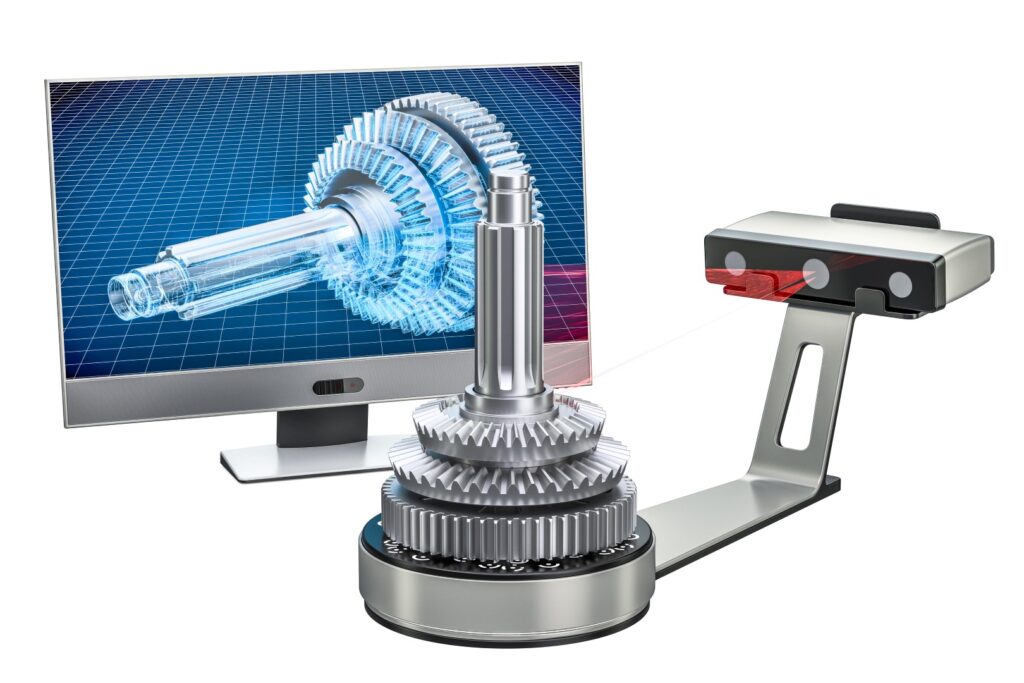
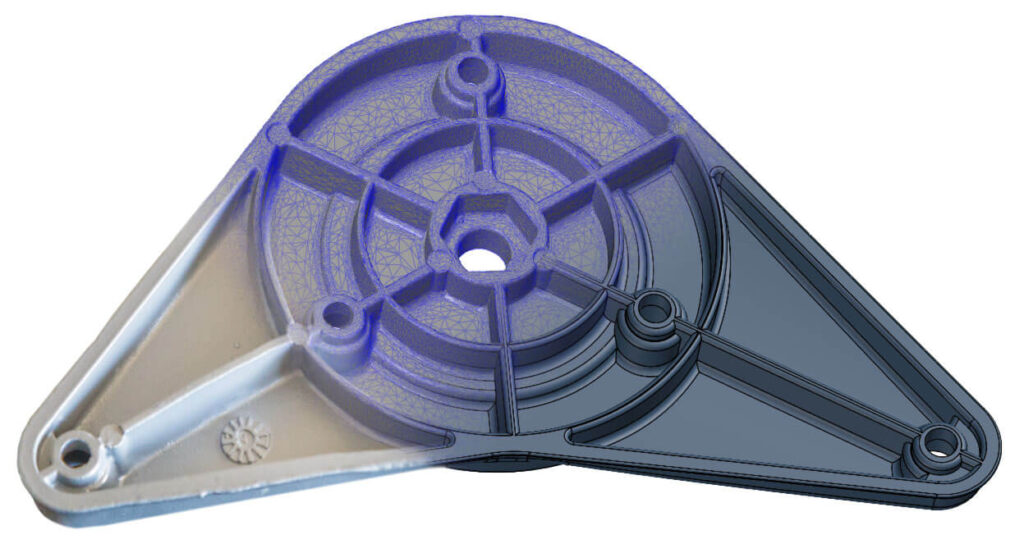
Reverse engineering technology has become a useful tool for creating a three-dimensional digital model of an existing physical part, thanks to the widespread availability of computer-aided design software. As a result, 3D CAD, computer-aided manufacturing, and other computer-aided engineering applications have become more accessible.
The main reason why design engineers are progressively using reverse engineering is that its hardware and software have become far more reasonable, allowing tech firms, particularly small businesses, to accelerate development and reduce the cost of production. Its software can also be seamlessly integrated with computer-aided design programmers.
Reverse Engineering – A tool to reinvent:
Reverse engineering, is one of the key methodologies used in a variety of industries, including aerospace, automotive, consumer electronics, medical devices, sports equipment, toys, and jewelry. It is also used in forensic science and accident reconstruction. In contrast to creation and innovation, which play more significant roles in invention, reverse engineering focuses on the process and study of reinvention.

Reverse engineering is essential in modern industry practices for a variety of use case scenarios:
- Replacing malfunctioning components
- Producing after-market spares or replacements
Numerous machines and instruments which are widely still in-use were manufactured before CADCAM. To avoid costly shutdowns and generation loss, any parts of this equipment that become damaged must be repaired or replaced as soon as possible.
Customers have a greater selection of replacement parts with aftermarket automobile parts. They also provide significant financial benefits to the customer, generally costing much less than the ‘official’ version.
Common applications across industries:
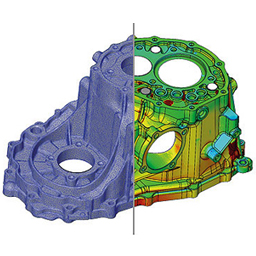
In the automobile industry, the important phases in reverse engineering are correctly and efficiently capturing the forms of the car body (mainly freeform) and extracting the information from the resulting scan in order to reconstruct the model as it can be used for any part of the vehicle, component or subsystem.
Medical Reverse Engineering (MRE) aims to leverage Reverse Engineering (RE) techniques to reconstitute 3D models of anatomical structures and biomedical objects for medical product design and manufacture, as well as BME research and development.
Heavy equipment reverse engineering involves evaluating the architecture, functionality, and operation methods of the equipment.
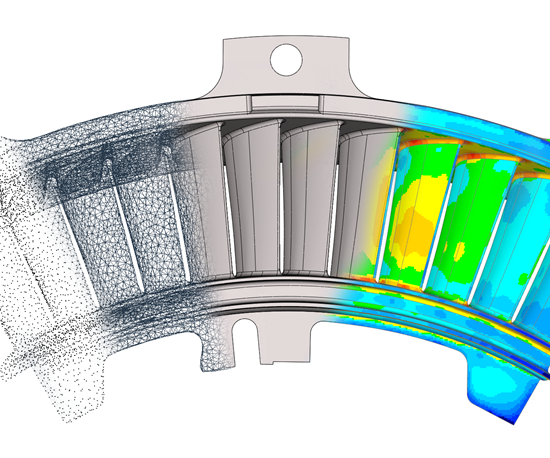
Reverse Engineering in the aerospace industry uses cutting-edge technology to produce accurate scans of both large and small parts examining the working process of each of the parts, which may then be used for the manufacturing of new parts and in finding optimized solution.
Questions to be asked before reinventing a product:
What is the objective of reverse engineering? (Or) Why reverse engineering is required?
The usual expectations when it comes for implementing Reverse Engineering include:
- It helps businesses grasp the system’s intricacies.
- It helps analysts create useful lost information regarding legacy systems.
- It can be used to discover reusable components for future examination and application.
- It assists in the generation of graphical representations of the system from various perspectives, such as ER diagrams, class diagrams, and DFDs, among others.
- It can identify any anomalies that may have occurred due to changes made to software over a period of time that could have led to unexpected errors or bugs.
Limitations of reverse engineering:
Because technology has advanced so quickly, some believe that reverse engineering can be as simple as waving a fast scan wand and returning an instant 3D model. Unfortunately, it isn’t that quick. There are numerous stages that require time along the process. The intricacy of your part or equipment will influence how long it takes to scan it. Furthermore, various scanners will work at different rates. It will also take longer if your assembly must be disassembled and each piece scanned individually.
DEP’s value-added engineering services
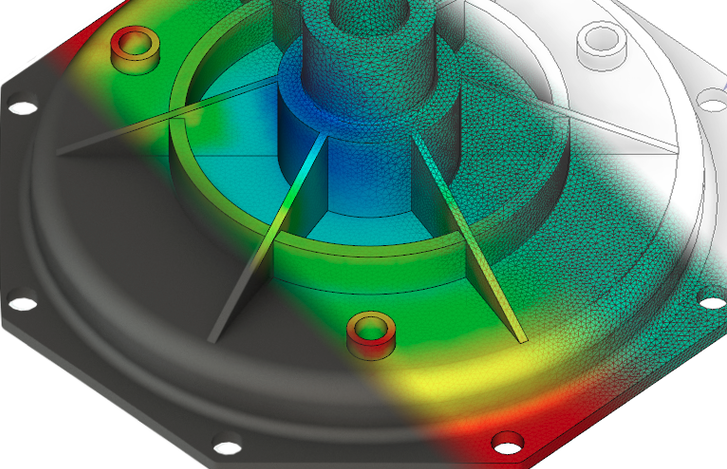
DEP, as an engineering technology business, provides reverse engineering services for many segments of products and equipment, allowing you to improve design while monitoring manufacturability and the development process. Our qualified engineering team is well-versed in these tasks, and our cutting-edge software tools ensure that the physical object models are ready for analysis, design optimization, or manufacturing. We provide reverse engineering support to customers at various stages of product development to discover the original design intent, modernize production processes, or create a new part to fit a legacy part, among other things.
- 3D laser scanning technology is used to precisely capture physical components.
- Scalable services to meet increasing engineering demands.
- Extensive reports and insights on the product’s features.
- Decades of expertise in the design phase to ensure the approach’ effectiveness.
- Prototyping and other modernized initiatives provide manufacturing support.
Conclusion
Reverse engineering is a satisfying and challenging process. It piques our interest by allowing us to see how professionally developed solutions are put into action. It allows us to disassemble and list each individual component in the time given for disassembly. This endeavor requires user dialogue and debate, as well as delegation of side aims, theories, and general conclusions. However, all of these efforts contribute significantly to the development of new variations of products based on the same concept.